CT Scan Center Ltd.
A CT scan can be used to examine every part of your body, including: Chest, belly, brain, sinuses, pelvis, arm, leg, liver, pancreas, intestines, kidneys, bladder, adrenal glands, lungs, heart, blood vessels, bones, and the spinal cord.
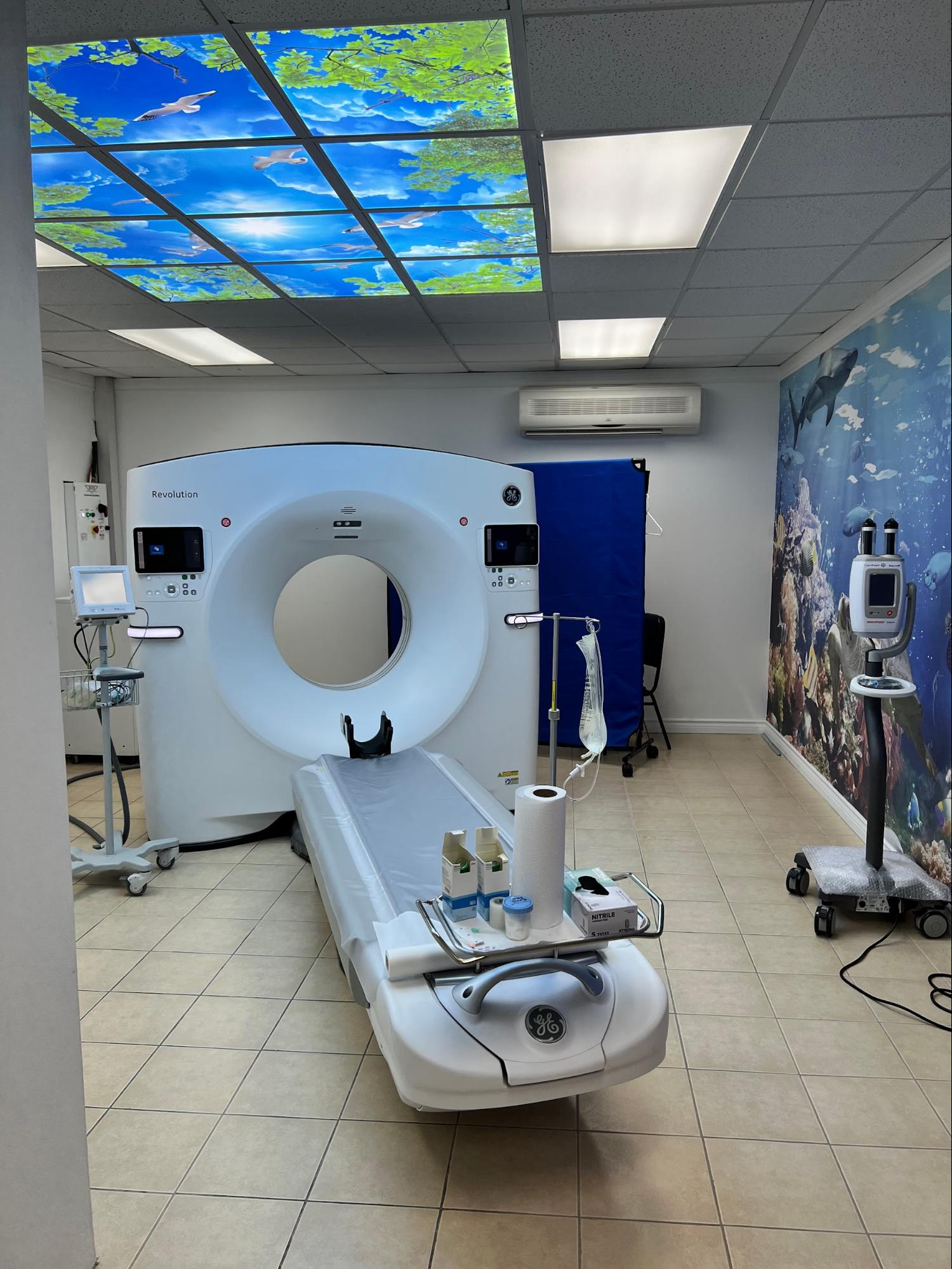
TIMT’s State-of-the-Art High Resolution 128 slice CT scanner is programmed with the most current protocols as recommended by the ACR. The 128-slice scanner is fast-speed and although the actual scanning time on the table takes less than a minute, patients should plan on minimum 30 minutes for their appointment. TIMT uses the lowest dose of radiation possible that still ensures a high-quality image.
TIMT tailors every CT exam to each patient while also minimizing repeat exams to ensure the lowest dose of radiation necessary. In fact, TIMT’s radiologists use the low dose CT protocol that is referenced by radiologists internationally!
The CT looks like a large donut with a narrow table. The tube will move around the body and collect images from a variety of angles. The CT technologist will perform the scan from the console room and will be able to always see and speak with you.
CT scans can be useful in many situations including:
- Diagnose muscle and bone disorders
- Pinpoint the location of a tumor, blood clot or infection
- Guide procedures such as radiation therapy, biopsy, and surgery
- Detect internal injuries or internal bleeding
- Detect and monitor diseases like cancer
- Some exams require a contrast to be injected into your arm during your exam. The time to complete a CT scan depends on the body parts being examined and whether you are required to have an injection of contrast. After the scan is finished, one of our US or UK trained, board-certified radiologist will interpret the study.
CT Cardiac Calcium Scoring
What is Cardiac Calcium Scoring?
Cardiac Calcium Scoring detects the buildup of plaque in blood vessels. Plaque, an accumulation of fat, calcium and other substances, can build up over time and cause a narrowing or blockage of the arteries. This buildup causes heart disease and can even cause a heart attack. The non-invasive Cardiac Calcium Scoring test is done using a CT (Computed Tomography) scan. It looks at the heart and evaluates a patient’s risk for developing coronary artery disease (CAD) by measuring the amount of plaque in the coronary arteries. A Cardiac Calcium Scoring exam is often a better indicator of coronary events than a cholesterol screening or other tests.
The Score
Your calcium score directly corresponds to your likelihood of having heart disease or a heart attack. The lower your calcium score and percentile rank, the less likely you are to experience a cardiac event. The calcium score itself, also known as an Agatston score, is based on the amount of plaque found via the CT scan. This number is then turned into a percentage.
Coronary/ Cardiac CT Angiography (CCTA)
What is Coronary/Cardiac CCTA?
Coronary/Cardiac Angiography (CCTA) is an imaging study used to identify blockages of the coronary arteries which are the blood vessels that supply the heart. These blockages – also called stenoses – are caused by atherosclerotic plaque that builds up in the wall of the arteries. Over time they can reduce or completely block blood flow, which in turn can cause serious health complications.
The CCTA test uses a computed tomography (CT) scanner and an intravenous (IV) injection of contrast, takes just a few minutes to perform, and is highly accurate for detecting blockages.
Am I a Good Candidate For CCTA?
It is important to talk about your risk factors with your health care professional. You may be referred for a CCTA if you have:
- Stable chest pain with low or intermediate risk of coronary artery disease (CAD).
- New or worsening symptoms (e.g. chest pain or shortness of breath) with a previously normal stress test result.
- Had an unclear or inconclusive stress test.
- New onset heart failure with reduced heart function.
The Test
A good quality CCTA examination requires that your heart rate is < 65-70 beats per minute. To help ensure a low heart rate at the time of the study, your doctor may prescribe you a small dose of oral medication to be taken one hour prior to arrival at our facility.
Once you arrive to our facility, a CT technologist will take you to the changing area to put on a gown and explain the procedure. An IV will be started in your arm and your heart rate and blood pressure will be measured. Based on these parameters, you may be given additional small doses of intravenous medication. Once your heart rate is satisfactory, we will bring you into the CT suite and have you lie face-up on the table. We will place a small nitroglycerin tablet below your tongue immediately before the CCTA exam which helps to dilate the coronary arteries.
The CT table will move slowly and the images will be taken as an IV contrast agent (“dye”) is administered. You may be asked to hold your breath at times and to lie as still as possible.
Even though the technologist will be in an adjacent room, they will be able to see you through a window and speak with you as well.
The entire test typically takes less than 10-15 minutes. Once completed, we will briefly monitor your heart rate and blood pressure. You will then be able to leave our facility.
What the Findings Mean
One of our radiologists with subspecialty training will analyze and interpret the images to identify the presence of coronary artery disease and the severity of any blockages that may be present. The radiologist will generate a report of the results which you will collect.
